Updated 10/27/2023
Google is arguably one of the best-known companies globally, and its search engine is so popular it has become a verb to google it. But it has other great products like Gmail, YouTube, Chrome, etc. To invest in a company like Google, we need to understand its business model and make money.
Although it is a tech company, the basic economic facts that drive the company make it easier to understand than we might think, and today, we will uncover how Google makes money.
A few years ago, Google changed its name to Alphabet to merge the different businesses under one umbrella and represent the different classes of stock ownership. Despite the name change, everyone still refers to the company as Google.
The company offers various software and internet-related services, including web search, browsing, streaming entertainment, cloud computing, and more. Google leverages all of these different platforms and services to generate revenue.
Google competes in a few different competitive industries against some of the biggest and best businesses globally: Amazon, Microsoft, Facebook, Apple, and Alibaba, among many others. Today, we will learn how Google competes and, in many cases, exceeds the performance of these other dominant global players.
In today’s post, we will learn:
- Brief History of Google
- How Does Google Make Money
- Breakdown of Google’s Ad Business
- Deeper Look Into Google’s Segments
Okay, let’s dive in and learn more about how Google makes money.
Brief History of Google
Today, Google is worth $1.95 trillion and has earned its place in the Merriam-Webster Dictionary as a verb, but its beginnings were far more humble.

Two men, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, both Ph.D. candidates when they met in 1996 while attending Stanford, came up with the idea of creating a search engine they originally intended to name “BackRub.” Yuck! I’m glad they didn’t go with that name.
One year later, on September 14, 1997, they officially launched Google.com. Fun fact: Milton Sirotta is responsible for the name Google. He took the name from googol, which refers to the number 1 with 100 zeros following it; they chose it to signify that the search engine would provide huge amounts of information.
Page’s and Brin’s main goal was to organize all possible information globally and organize it as an index.
Page and Brin took their first $100,000, donated by Sun co-founder Andy Bechtolsheim, and began developing the search engine in 1998, with the two men starting the operation in a garage in Palo Alto. But after a year, the company had outgrown that garage and needed to move to their first office space.
The search engine proved immensely successful, prompting the move to Mountian View in 2003. During this time, Google launched several successful products such as:
- Google News (2002)
- Gmail (2004)
- Google Maps (2005)
- Google Chrome (2008)
While developing the search engine, Brin and Page created the PageRank algorithm, which ranked websites based on a particular set of parameters. That creation revolutionized internet search by ranking search results according to the number of links to a particular page, helping improve the page’s usefulness to the search.
In 2000, Google began selling ads linked to particular search keywords; the initial ads were text-based to help maintain an uncluttered page design and maximize page speed. That set the groundwork for the success Google enjoys today.
In 2004, Googe went public, with the stock price almost quadrupling.
Despite Google making the majority of its income from advertising through its IPO in 2004, it didn’t embrace HTTP cookie-based web tracking until 2007, with the purchase of DoubleClick for $3.1 billion. That purchase allowed Google to start making use of cookie-based tracking.
In 2006, Google acquired YouTube for $1.65 billion, which launched its first video in 2005. YouTube has become one of the best investments Google has ever made, but more on that now.
Other acquisitions and investments along the way have improved the operations and growth of Google, such as the growth in AI, Cloud, and many others.
How Does Google Make Money?
Alphabet, or as we all know them, Google began in 1998 and has grown to become the undisputed king of internet search, so much so that “googling” is now a verb as first established by the Oxford Dictionary in 2006. The search function now controls over 80% of global search queries. All of which allows Google to generate strong revenue growth and cash flow.
Like Apple and Microsoft, Google’s ecosystem strengthens as its products are adopted by more and more users, making its online advertising services more attractive to advertisers. These network effects help increase ad revenue, which could grow into double-digit rates for the foreseeable future.
Google uses its tech expertise and innovation to improve the user experience across its platforms. All of this makes the sales and purchases of ads even more efficient for publishers and advertisers, along with the increased adoption of mobile usage.
Google operates across three different segments, as reported on their financials:
- Google Services
- Google Cloud
- Other Bets
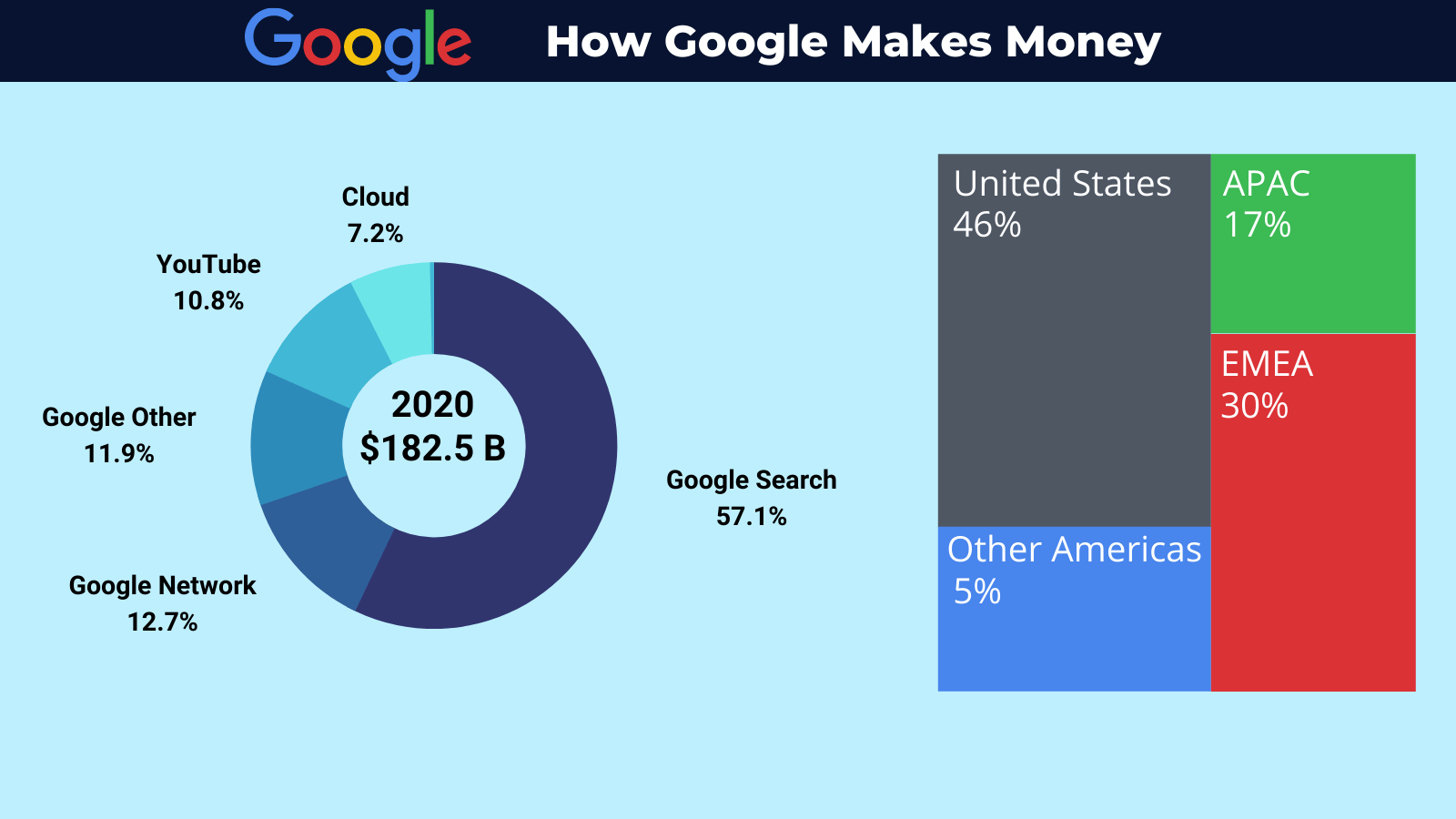
Google’s search segment generated revenues of $146 billion in 2020 and, for the first nine months of 2021, $148 billion. Google Cloud earned $13 billion in 2020 and $13.6 billion in the first nine months of 2021.
Over the last few years, Google has earned a large percentage of its revenues from the Ad business or Google Services, including search, Chrome, YouTube, and many others.
- 2020 = 80%
- 2019 = 83%
- 2019 = 85%
As we can see, over the last three years, the mix of revenue growth has been shrinking for ad revenue, but that indicates that Google is expanding its revenues from other sources, such as Google Cloud.
Breakdown of Google’s Ad Business
Google Services includes products and services such as ads, Android, Chrome, hardware, Google Maps, Google Play, Search, and YouTube. Google Services generates revenues primarily from advertising, sales of apps, in-app purchases, digital content products and hardware, and fees received for subscription-based products such as YouTube Premium and YouTube TV.
The Google services segment gives the company a tremendous moat, especially YouTube and Search. The key to $GOOG’s success is its use of AI to answer everyday questions, which helps consumers choose what to search for next.

Google is utilizing MUM (Multitask Unified Model), which combines multimodal inputs like language, images, and videos with the ability to understand implicit connections using context. All of this is game-changing in search and advertising.
People rely on videos, language, images, and context to understand information, but computers are a big challenge. That makes MUM so revolutionary; it can understand information simultaneously across various formats, like video and text.
Google Search VP Pandu Nayak recently explained how Google is using AI to answer these everyday questions:
“People rely on language, images, videos, and context to make sense of information. But this is a huge challenge for computers. Of course, AI models today can know a lot of things, like this is a description of a lion. This is a photo of a lion. And this is the sound a lion makes. But to really grasp what a lion is, you need to understand the relationship between all of this information and then some. Like the notion that while a lion is a cat, that doesn’t make it a good pet. And that’s what makes MUM revolutionary. It’s one of our first AI models that is truly multimodal, which means it can simultaneously understand information across a wide range of formats, like text, images, and video. MUM can also draw implicit connections between concepts, topics, and ideas about the world around us.”
Google Search VP Pandu Nayak
Google Search is the global leader with approximately 92%, but Microsoft Bing comes in with 2.66%. Considering all search engines, including e-commerce and video, the 2nd largest is YouTube, with 2.29 billion users behind Facebook’s 2.85 billion. Google Chrome has the largest market share, with 65%.
To encourage competition at the top of Google pages, Google employs a bidding system to gain the top spot in Google ads. Advertisers bid against each other to gain the top spot, with the winner or highest bidder awarded the top spot where lower bids or the lowest bid aren’t displayed.
The advertisers pay Google each time a visitor clicks on an ad, with each click worth anywhere from a few cents to over $50 for the most competitively searched terms, including loans, insurance, and other financial services.
And, if you are an advertiser, you want to spend most of your advertising dollars where your customers are: Google Search, Chrome, and YouTube. Combine these network effects with groundbreaking AI, and you have a near-monopoly.
The Google AdSense program enables non-Google sites to embed Google display ads on their pages. The AdSense ads work in the same ways as Google onsite ads, but they display them on Google-approved sites anywhere on the net.
An important consideration regarding Google’s ad reach is that their ad integration crosses almost the whole universe of Google, from any website recommendations when we use Gmail, YouTube, Google Maps, and any other Google sites. These are all sources of revenue generation for Google. It all reaches beyond search or Chrome, and as more and more of these sites gain more adoption, it expands the ad revenue generation opportunities.
The Android operating system also includes the Services segment, which has the largest global market share with the smartphone duopoly of Android OS and Apple iOS. Android currently owns approximately 72% of the market, with Apple owning 26%. One reason is that Android is open-source and free to all users.
Google doesn’t earn revenues from the Android OS; instead, it earns revenues from the Google Play store and ads placed in search, Chrome, YouTube, third-party websites, and Apps on Android smartphones.
Google’s primary growth driver will come from advertising, and industry analysts expect that digital advertising will continue to grow steadily between now and 2024. Digital ad spending expects to grow from 60% to 68% by 2024.
All our time on search engines, websites, YouTube, and third-party sites provides Google with additional opportunities. The trend is expected to accelerate because we spend all our time on devices instead of traditional media like TV.
Most advertisers spend their budgets on Google and Facebook because they have the most engaged users, with Amazon a distant third. Google and Facebook have 27% and 25%, respectively, with Amazon at 9.5%.
Deeper Look into Google’s Segments
The other two segments of Google’s business are Cloud and Other Bets; let’s look at the Cloud first.
The cloud computing market will continue to grow, especially Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) and Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), because of the continued adoption of cloud computing globally. The pandemic accelerated this trend as businesses realized a need to be flexible and adaptable.

Many businesses are investing a large part of their IT spending in the cloud; for example, instead of building data centers in-house, businesses embrace data centers, and infrastructure could be provided by the big 3: Amazon, Microsoft, and Google.
As of 2nd Q 2021, Amazon AWS has a market share of 31%, Microsoft Azure has 22%, and Google has 8%. Analysts expect that the spending on public cloud computing will grow to exceed 45% of all enterprise IT spending by 2026, up from 17% in 2021.
Google’s Cloud business is currently unprofitable, but as the company is scaling up this segment’s revenues, the company is on pace to become profitable next year. Personally, I don’t expect them ever to overtake either AWS or Azure as these two have too big of a lead, but they should provide additional profits to Google for many years.
Google Cloud has grown revenues:
- 2018 – $5,838 million
- 2019 – $8,918 million
- 2020 – $13,059 million
Those are phenomenal growth rates, and the current run rate for 2021’s revenues is close to $20 billion-plus. The platform is on the way to becoming profitable on the same level as Amazon’s AWS at 30% operating margins.
The Other Bets segment contains several different operations that are not producing much revenue for Google. Two known operations are Waymo, the self-driving business, and Stadia, the cloud-gaming platform.
Most of the revenues generated for this segment stem from the sale of internet services, plus some licensing and R&D services.
Other Bets is a money sink as of right now, with the segment losing upwards of $1.3 billion in 3rdQ21 and over $3.8 billion in losses during the first nine months of 2021. On the revenue side, Other Bets contribute negligible revenues to the overall performance of Google:
- 2018 – $595 million
- 2019 – $659 million
- 2020 – $657 million
Investor Takeaway
Google search and Chrome control around 80% of all search activity on the net, which helps Google control the digital ad revenues they generate. And because of the adoption of the search engine, they have created a wide-moat business with huge network effects, which are evident in the ad business.
In the third quarter of 2021, the company grew profits by 68%, which is unheard of at the size of the company and is more evidence that Google carries a wide moat around its search engine and advertising business. Combine that with the popularity of search, YouTube, and the Android operating system, and you have a company poised to profit for many years.
Understanding how Google makes money gives us better insight into any investment with the company. Predicting the revenue streams becomes easier once you understand the business model.
Even though Google is a tech company, you don’t have to be a tech insider to understand the business model or the deeper meaning behind the different levels of AI, machine learning, and deep learning.
Because of the nature of its asset-light business, the company generates tons of free cash flow, which helps it invest a lot of money into R&D to maintain its technological edge and continue to improve its products and services.
The advantages make Google one of the premium businesses in the market with a long runway to growth and profitability.
And with that, we will wrap up our discussion on how Google makes money.
As always, thank you for taking the time to read today’s post, and I hope you find something of value. If I can further assist, please don’t hesitate to reach out.
Until next time, take care and be safe out there,
Dave

Dave Ahern
Dave, a self-taught investor, empowers investors to start investing by demystifying the stock market.
Related posts:
- How Visa Makes Money: A Business Model Breakdown Updated 10/12/2023 Visa Inc (V) is one of the leading payment brands globally and its cousin Mastercard (MA). Visa provides payment services to over 200...
- Saas Companies: Simple and Powerful Business Updated 11/9/2023 In 2021, analysts estimated the subscription as a service (SaaS) market size to be around $145.5 billion in the U.S. alone, with expectations...
- Applying the Lessons of Enron’s Mark-to-Market Accounting Scandal Today It may be surprising, but companies today are still using the same mark-to-market accounting that led to Enron’s fraud and bankruptcy in 2001. Mark-to-market accounting...
- Business Breakdown: An In-Depth Netflix Stock Valuation The Netflix product is easy to understand for most investors. Doing an in-depth stock valuation can be much harder. In this post, I will show...
