Understanding the ISP (Internet Service Provider) industry is crucial for investors. ISPs are the backbone of our digital world, connecting us to the internet and offering various online services. By studying the ISP industry, investors can make informed investment decisions.
To invest in the ISP sector, knowing how ISPs operate, their services, and their market presence is important.
Key players like Verizon, AT&T, Comcast, and Charter shape the industry and affect investment outcomes.
By digging deeper into the key players, we can find potential investments. Understanding their financials, market positioning, and investments can give us an advantage.
Also, staying on top of tech advancements, regulations, and competitors can help investors.
Today’s post aims to give investors an overview of the ISP industry. We will focus on the industry’s what, why, and how and look deeper into the key players and their prospects. We aim to provide helpful information so you can make informed choices in the ISP industry.
In today’s post, we will learn:
- What is An ISP?
- Roles of ISPs in Providing Internet Connectivity
- Types of ISPs
- Overview of ISP Marketplace
- Key Players in ISP Industry
- Future of the ISP Industry
Okay, let’s dive in and learn more about the ISP industry.
What is An ISP?
ISPs, or internet service providers, offer access to the internet. ISPs can provide access to the internet through various means. Most people access the internet through DSL, cable, wireless, and fiber optics.

The ISPs are responsible for making sure we can access the internet. They also route internet traffic, resolve domain names, and maintain the network infrastructure.
The main gist is that ISPs allow individuals and businesses to access the internet.
All the while, they are providing infrastructure, reliable speed, and overall reliability.
ISPs can offer other services, such as:
- Domain Registration
- Web hosting
- Browser services
The internet inventors originally designed it to work with government agencies and specific universities. But in the 1980s, they developed access for the general public via the World Wide Web (WWW).
At first, ISP providers had limited access to a few; AOL (America Online) being the most famous.
These first forays into the web used dial-up connections via a phone line. Those old enough remember that awful connection sound and the movie War Games with a young Mathew Broderick.
During the 1990s, the number of ISPs exploded from a few to several thousand, and the internet boomed.
This was the early days of the Internet, but as connectivity increased and speeds increased beyond the dial-up days, the Internet economy began.
Roles of ISPs in Providing Internet Connectivity
ISPs are crucial in providing internet connectivity to individuals and businesses. They serve as the bridge between users and the vast world of online information and services.

ISPs are responsible for ensuring users can access the internet reliably and efficiently. Access to fast internet is increasingly seen as a utility – like water and gas – necessary to function.
ISP’s function by establishing and maintaining the infrastructure necessary for internet connectivity. They invest in physical infrastructure, such as cables, routers, and servers, that form the backbone of the internet. These infrastructures often interconnect through a complex network of data centers and transmission lines spanning vast geographical areas.
When a user subscribes to an ISP’s services, the ISP assigns a unique IP (Internet Protocol) address to that user. The IP address acts as a digital identifier, allowing data to be sent and received over the internet. ISPs also provide users with modems or routers, enabling a connection between their devices and the ISP’s network.
Once connected, users can access websites, send and receive emails, stream videos, download files, and engage in various online activities.
ISPs are responsible for delivering the requested data packets between the user’s device and the desired destination on the internet. They ensure the data transmits accurately and on time, enabling seamless communication and information exchange.
ISPs offer different types of internet connections, including:
- Broadband
- DSL
- Cable
- Fiber-optic
- Wireless options
Each type of connection has its own speed, reliability, and availability characteristics. ISPs also offer various service plans tailored to meet different user needs, including different levels of bandwidth and data usage limits.
Furthermore, ISPs are responsible for maintaining network security and protecting users’ data and privacy. They employ firewalls, encryption, and anti-malware systems to safeguard their networks and customers’ information from cyber threats.
In summary, ISPs are the essential facilitators of internet connectivity. Through their infrastructure, services, and network management, ISPs enable users to access and utilize the internet for various purposes, enriching their personal and professional lives.
Types of ISPs
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) come in various types, offering users different internet connectivity modes.

Broadband ISPs are among the most common types. They provide high-speed internet access through various technologies like DSL (Digital Subscriber Line), cable, fiber-optic, and satellite connections. DSL and cable connections transmit data using existing telephone or cable TV lines.
On the other hand, fiber-optic connections use thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit data as pulses of light, allowing for incredibly fast speeds. Satellite connections rely on signals sent to and received from satellites in orbit, making them accessible in remote areas.
Dial-up ISPs were prevalent in the past but are less common nowadays. They utilize telephone lines to establish an internet connection. Dial-up connections remain slower when compared to broadband, and they tie up the phone line while in use. As technology advances, dial-up has become less popular due to its limited speed and availability. Many rural areas still rely on dial-ups to access the internet, but satellite services like Elon Musk’s Starlink are changing that.
Wireless ISPs (WISPs) provide internet access using wireless technologies such as WiFi, microwave, or cellular networks.
WISPs enable users to connect to the internet without needing physical cables. WiFi is commonly used in homes, cafes, and public spaces, while microwave and cellular networks offer internet access in specific areas or on the go.
Satellite ISPs utilize communication satellites to provide internet access to remote areas where traditional broadband infrastructure is limited or absent.
Satellite ISPs enable users to access the internet regardless of location, but they may have higher latency and limited bandwidth than other ISPs.
Each ISP type has advantages and limitations regarding speed, availability, and cost. For example, satellite ISPs offer good connectivity in static locations. If a user tries to access the internet from a car, the connection is not as good as a home.
Recently, President Biden announced plans to allocate $42.5 billion to build out high-speed networks. The plans focus mostly on rural areas or areas where the service is slow.
This outlines the need for internet connectivity and high-speed access to grow the economy and improve living conditions.
“Data from Pew Research Center found that only 77% of US adults reported having a broadband connection at home — with just 64% of the older (65+) generation reporting access, leaving more than one third without home broadband. Interestingly, the next age group least likely to have broadband at home are 18-29 year olds — that age group was found to be reliant on their smartphones, substituting fixed access for phone data.
Lacking access to high-speed internet at home is one thing, but perhaps most shocking of all is that 7% of American adults report no usage of the internet at all (as of 2021).”
The above highlights the importance of the ISP industry.
Overview of ISP Marketplace
The ISP market contains diverse players, including national, regional, and local providers. Prominent companies like Verizon, AT&T, Comcast, and Charter dominate the market, offering widespread coverage and various service options.
These established players have well-developed infrastructure, extensive customer bases, and strong brand recognition. Evaluating their financial performance, market share, and customer satisfaction can provide valuable insights for potential investors.
Beyond the industry giants, regional and local ISPs also play a significant role in serving specific geographic areas. These smaller providers often focus on niche markets or underserved communities, offering personalized services and localized customer support.
Investing in such ISPs may provide opportunities for growth in specific regions or market segments.
In recent years, the ISP market has witnessed technological advancements that impact the investment landscape.
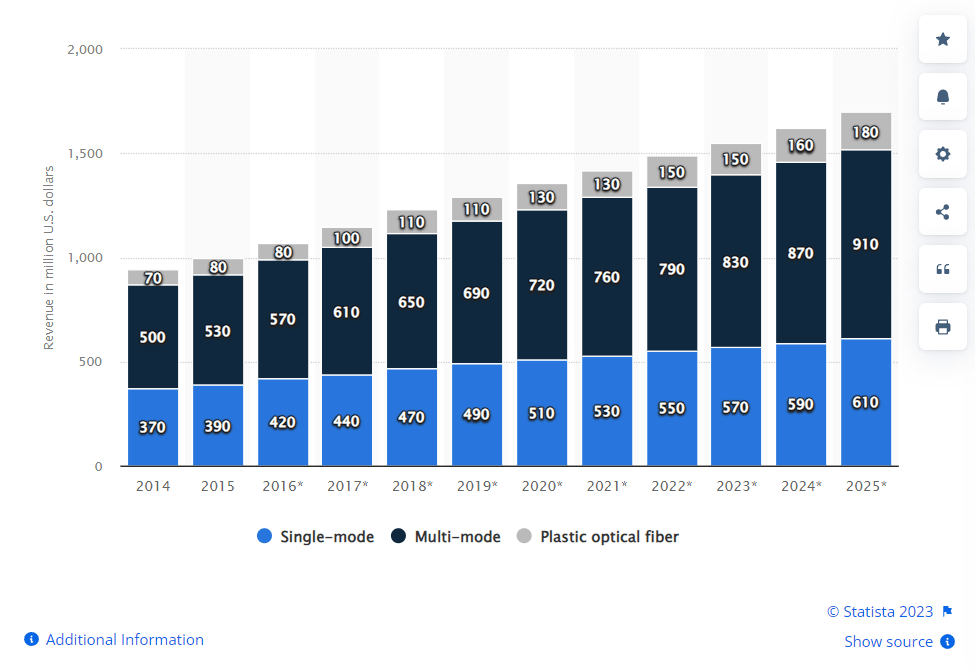
The deployment of fiber-optic networks, the development of 5G technology, and the expansion of wireless connectivity have opened up new possibilities and increased competition.
Another tech breakthrough includes small cells.
What are small cells?
Small cells are compact wireless base stations that play a vital role in the ISP industry. These small cells are deployed in densely populated areas to enhance network capacity and coverage.
With the ever-increasing demand for data and the proliferation of mobile devices, small cells provide a solution to alleviate network congestion and improve connectivity. They enable ISPs to deliver faster and more reliable internet services to users in crowded urban areas, stadiums, shopping centers, and other high-traffic locations.
Small cells are instrumental in expanding network capacity, improving signal strength, and ensuring a seamless user experience, making them crucial components in meeting the growing connectivity needs of today’s digital world.
To learn more, check out Crown Castle’s Small Cells 101.
Regulatory factors also influence the ISP market. Government policies and regulations on net neutrality, data privacy, and infrastructure development can significantly affect ISPs and their investment potential.
Furthermore, customer preferences and demands are evolving, with users seeking faster speeds, reliable connections, and enhanced customer experiences.
Key Players in ISP Industry
The four key players in the ISP industry include:
- Verizon
- AT&T
- Charter
- Comcast

Verizon is a prominent player in the ISP industry, offering a wide range of services to individual consumers and businesses. The company provides internet connectivity, voice, and TV services through its Fios fiber-optic network. With Fios, Verizon delivers high-speed internet access, crystal-clear voice calls, and an extensive selection of TV channels.
In addition to residential services, Verizon caters to businesses with its Verizon Business division. This division offers enterprise-grade solutions, including internet connectivity, network security, cloud services, and managed IT solutions. Verizon Business serves various industries, supporting their digital transformation and connectivity needs.
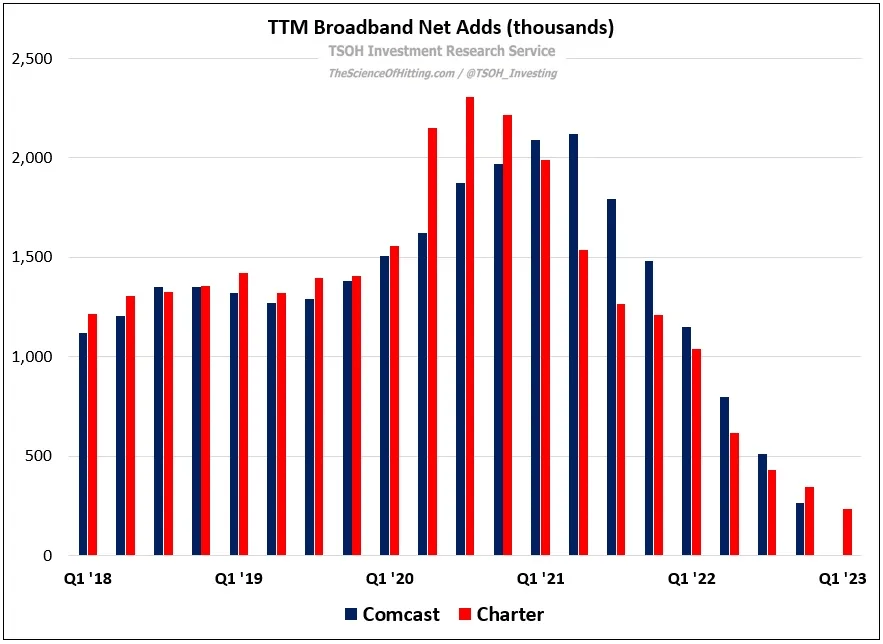
Verizon holds a strong market presence in the ISP industry with a market cap of $149.2 billion. In 2022, Verizon generated $136.8 billion in revenue with over 1.1 million new broadband customers equaling 111.2% growth over the past four years.
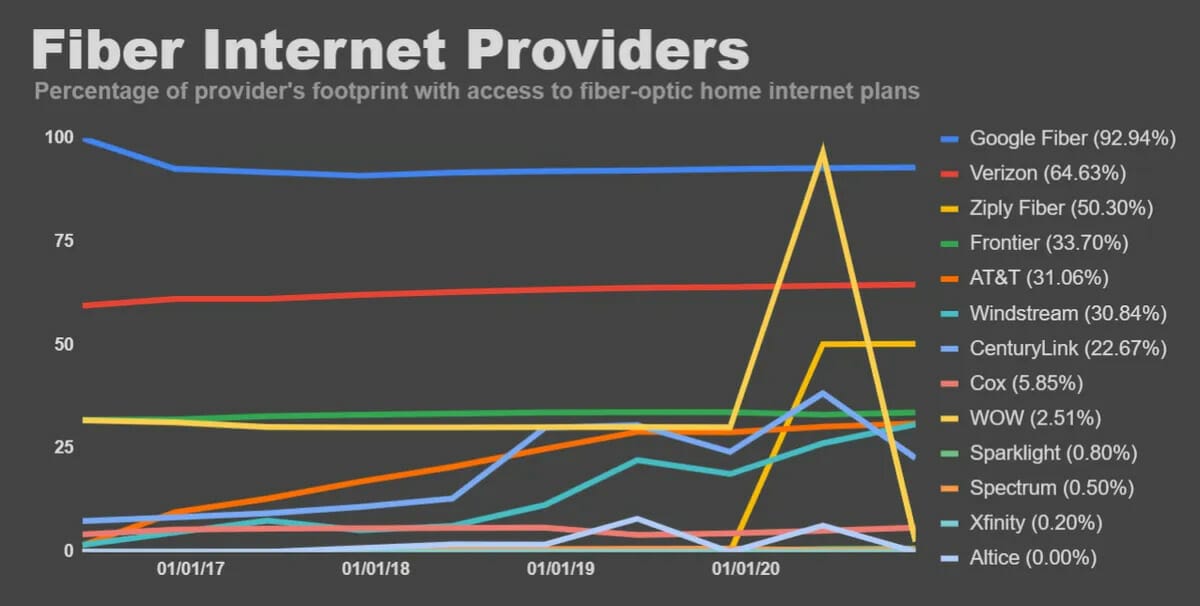
As one of the largest telecommunications companies in the United States, it has established a substantial customer base and a widespread network infrastructure. The company has significantly invested in expanding its fiber-optic network, aiming to provide customers faster and more reliable connectivity.
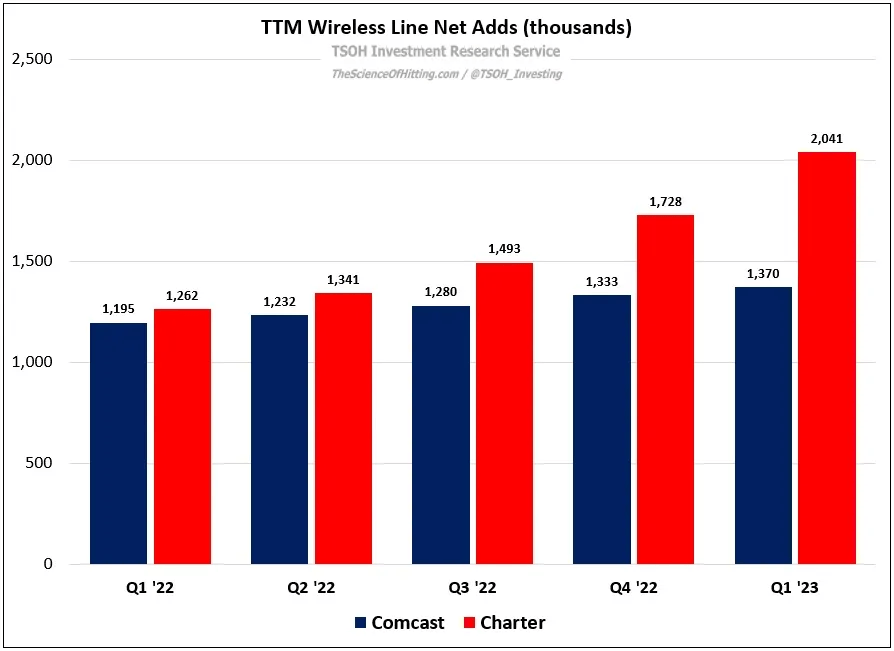
Their capex or investments in 5G over the past four quarters equals $23 billion, far larger than the cable providers Comcast and Charter. The additional investments allow Verizon to scale its WiFi capabilities compared to the cable providers.
Verizon has been at the forefront of 5G technology development and deployment. 5G offers significantly faster speeds, lower latency, and increased network capacity compared to previous generations.
Verizon has been rolling out its 5G network across various cities, bringing the benefits of this next-generation technology to consumers and businesses. 5G has the potential to revolutionize industries, enabling advancements in areas such as autonomous vehicles, remote healthcare, and smart cities.
Small cells play a crucial role in Verizon’s future growth strategy.
These compact wireless base stations are deployed in dense urban areas to enhance network capacity and coverage. Small cells enable Verizon to address network congestion, improve connectivity in crowded areas, and ensure a seamless user experience.
By leveraging small cells, Verizon can expand its network capacity and deliver faster and more reliable internet services to meet the increasing demands of data-hungry applications and devices.
Side note: Verizon accesses many of its small cells through leases with Crown Castle, the cell phone tower REIT.
AT&T is a prominent player in the ISP industry with a market cap of $110.4 billion and revenues of $120.7 billion in 2022, offering a wide range of services to consumers and businesses alike.
The company provides internet connectivity, phone, and TV services through various offerings. AT&T’s internet services include DSL, fiber-optic, and wireless options, catering to different customer needs and geographic locations.
AT&T has a strong market presence in the ISP industry, serving millions of customers across the United States.
The company operates an extensive network infrastructure encompassing wired and wireless technologies. This allows AT&T to provide widespread coverage and reliable connectivity to its customers.
Regarding 5G impacts, AT&T has been actively working to deploy its 5G network across the country. 5G is the next-generation wireless technology that offers faster speeds and lower latency.
The company has invested a staggering $140 billion into infrastructure in the past five years.
AT&T continues to lead the nation as the most extensive fiber internet provider while enhancing America’s “most reliable” 5G network.
They have grown fiber broadband connections from 2.76 million to 7.22 million, a growth of 27.4%.
These investments have led to over 160 million people covered by AT&T’s 5G network. Domestic wireless service revenues were up 5.2% and had strong mobility operational performance. Consumer broadband revenues were up 7.3%.
Charter is a prominent ISP with a market cap of $49.1 billion and 2022 revenues of $54 billion. The company provides internet connectivity, TV services, and phone services. Charter’s internet services include cable and fiber-optic options, delivering high-speed and reliable connectivity to customers.
With a strong market presence, Charter serves millions of customers across the United States. The company operates in various regions and is known for its brand, Spectrum. Charter has built a robust network infrastructure, enabling widespread coverage and reliable internet services.
While Charter is primarily known for its cable internet offerings, the company has expanded its internet customers by over 40% in the last eight years and 10.3% in the last three years.
Fiber-optic technology is also a significant focus for Charter’s future growth. Charter’s investment in fiber-optic infrastructure is to the tune of $5.5 billion, which they expect to conclude in 2025. These investments enable the company to expand its footprint and provide advanced internet services to residential and business customers.
Charter’s biggest headwind is subscribers switching to wireless services from Verizon and AT&T, but as those slow, Charter expects to grow as their network finishes its build-out.
Comcast is another leading ISP that offers a comprehensive range of services to consumers and businesses. Comcast’s Xfinity brand delivers high-speed internet through various technologies like cable and fiber-optic connections.
Comcast holds a significant market presence in the ISP industry, with a market cap of $166.7 billion and 2022 revenues of $121.4 billion. Comcast currently carries the largest market cap of the Big Four ISPs.
Comcast operates an extensive network infrastructure, providing its customers with widespread coverage and reliable connectivity.
Together with Charter, Comcast operates as a duopoly in their respective areas, with the companies splitting the U.S. in two, with less than 1% of customers having access to their services.
The duopoly is evident in access to broadband services. The Institute For Local Self-Reliance report found that the two ISPs hold an “absolute monopoly” over 47 million customers. Comcast remains the sole provider of internet services for over 30 million people.
On the upside, Comcast’s broadband services remain superior to competitors through their modems (DOCSIS 3.0 and 3.1).
On the ISP side, these investments in creating faster speeds through better tech have helped give Comcast a moat, and analysts expect broadband subs to increase over time.
Future of the ISP Industry
The global ISP market expects to grow considerably between 2023 and 2030. The market grew at a steady rate in 2022.
Some key trends driving the growth of the global ISP market include:
- Increasing virtualization in the IT sector
- Growth in demand for data centralization
- Rising data security concerns across all data-sensitive companies
The global ISP market expects to increase from $498.6 billion to $644.8 billion by 2028. Grand View Research predicts a 9.6% CAGR between now and 2030 and estimates the global market will hit $875.1 billion by 2030.
Analysts estimated the global broadband services market size would reach $419.4 billion in 2022 and expect it will reach $457.6 billion in 2023.
Much of the future growth will depend on the continued expansion of data and the growing need for data. Someone said recently, “Data is the new oil.” And they were right; data will drive the economy forward.
And the need for greater amounts of data plus speed will continue to drive the ISP industry. The providers will need to provide greater and greater connectivity plus speed, pushing the expansion of 5G, plus small cells and WIFI capabilities.
AI and expanding these services will help drive the ISP industry forward too. For example, as the need for more data centers continues to rise, so will the need for high-speed cabling and internet to connect these services.
Companies like Crowdstrike and Cloudflare, which operate in the security/connectivity sectors, will require faster connections and bigger data capabilities, i.e., ISP providers.
The pandemic accelerated the need for greater internet access, and the internet economy continues to take more share of the economy.
Other areas of growth include:
- Telehealth
- Hybrid Work
- Remote education
- Online shopping
- Connected gaming
Investor Takeaways
Investing in ISPs offers a lucrative opportunity to tap into a thriving market driven by the increasing demand for internet connectivity.
With more people relying on the internet for communication, information, and business transactions, ISPs play a vital role in connecting individuals and organizations worldwide.
The ISP industry provides various services, including internet access, voice, and TV. These services generate steady revenue streams, making ISPs attractive investment options. Established players like Verizon, AT&T, Comcast, and Charter dominate the market, offering widespread coverage and diverse service options.
These companies possess strong brand recognition, extensive customer bases, and well-developed infrastructure, making them appealing investment prospects.
Emerging technologies such as 5G and fiber-optic networks further contribute to the investment potential of ISPs. 5G technology promises faster speeds, lower latency, and increased network capacity, paving the way for transformative applications and services. Fiber-optic networks, known for their superior speed and reliability, provide opportunities for ISPs to expand their reach and meet the growing demands of data-intensive applications.
In summary, the ISP industry presents a promising investment opportunity. With the increasing reliance on internet connectivity, ISPs are essential for individuals and businesses.
And with that, we will wrap up today’s discussion.
Thank you for taking the time to read today’s post, and I hope you find something of value. If I can further assist, please don’t hesitate to reach out.
Until next time, take care and be safe out there,
Dave
Related posts:
- A Beginner’s Guide to Cloud Computing What is cloud computing? How does the cloud work? To invest in companies such as Microsoft, Shopify, Google, or Crowdstrike, we need to understand the...
- Exploring the Value Chain for the Pharma Industry Investing in any sector/industry can offer many different challenges. You can often come across a company you like but find another in the value chain...
- Warren Buffett’s Railroad Investment Updated 9/15/2023 2007, Warren Buffett revealed he had bought over 60 million shares in Berkshire’s first railroad. Buffett continues as our generation’s greatest investor. And...
- Guide to Investing in the Pharma Industry Did you know the revenues for the global pharmaceutical markets in 2022 equaled $1.48 trillion? It had grown from $390 billion in 2002, a CAGR...